Setting Up VIPs for NFS
You can set up a pool of NFS servers on various nodes in your cluster and connect to them using virtual IP addresses (VIPs) to achieve HA with failover; if one node fails, the VIP will automatically be reassigned to another NFS node in the pool. If you do not specify a list of NFS nodes to form a pool, then MapR uses any available node running the MapR NFS Gateway service. VIPs are not assigned to any nodes that are not on the list, regardless of whether they are running NFS.
The following illustration shows three nodes (Host1, Host2, and Host3) acting as NFS servers. Each node has two NICs whose ports are labeled eth0 and eth1. The NICs are grouped into two subnets, called Subnet A and Subnet B. Clients can access any of the NFS servers through a pool (or range) of VIPs assigned to each subnet. MapR assigns each VIP address in the pool at random to a MAC address in the subnet (with its corresponding physical IP address).
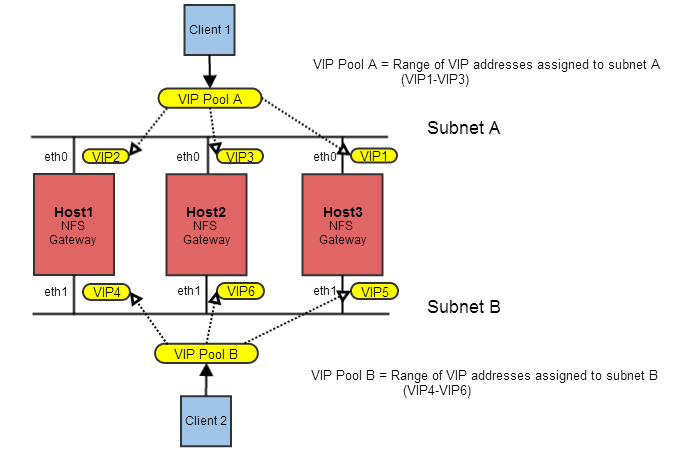
The initial VIP assignment shown above is summarized in the following table. If one NFS server becomes unavailable, the VIP assigned to that server is automatically assigned to another server on the same subnet.
| Server | Subnet | VIPs (randomly assigned) |
|---|---|---|
| NFS1 | A | VIP2 |
| NFS2 | A | VIP3 |
| NFS3 | A | VIP1 |
| NFS1 | B | VIP4 |
| NFS2 | B | VIP6 |
| NFS3 | B | VIP5 |
If the cluster's NFS nodes have multiple network interface cards (NICs) connected to different subnets, you should restrict VIP assignment to the NICs that are on the correct subnet: for each NFS server, choose whichever MAC address is on the subnet from which the cluster will be NFS-mounted, then add it to the list.
If you add a VIP that is not accessible on the subnet, then failover will not work.
You can only set up VIPs for failover between network interfaces that are in the same subnet. In large clusters with multiple subnets, you can set up multiple groups of VIPs to provide NFS failover for the different subnets.
VIPs are evenly distributed across NFS nodes. For example, if six VIP addresses are available for three NFS servers, two VIPs are assigned to each server. If the previous example did not have two separate subnets, the six VIP addresses might be assigned like this:
| Server | VIPs (randomly assigned) |
|---|---|
| N/FS1 | VIP1, VIP3 |
|
NFS2 |
VIP4, VIP5 |
| NFS3 | VIP2, VIP6 |
You can set up VIPs with the virtualip
addcommand, or using the Add Virtual IP dialog in the MapR
Control System.