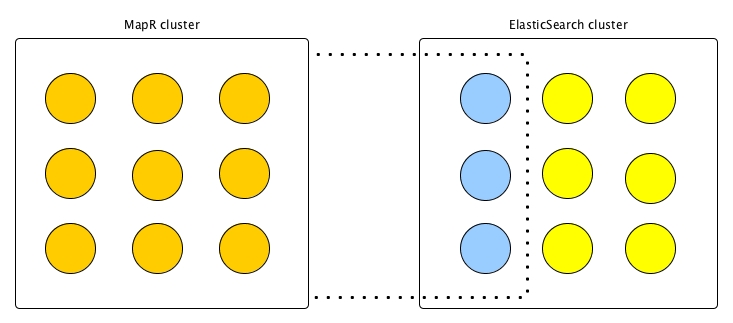
Gateway Placement for Elasticsearch Indexing
This topic describes several gateway topologies used for replicating MapR data for Elasticsearch indexing.
The following diagrams illustrate the different choices there are in where to place gateways. In each diagram there are two clusters: a source MapR cluster where the tables being indexed are located, and the Elasticsearch cluster where the corresponding types are located. Each cluster consists of 9 nodes, the MapR cluster with nine MapR nodes (in orange) running the MapR filesystem and storing table data, and the Elasticsearch cluster with nine nodes (in yellow) storing shards of the index where the types are located. Nodes where gateways are running are depicted in blue.
Gateways on the Source MapR Cluster
In the first diagram, the gateways are installed on three of the nodes in the MapR
cluster. If you use this topology then the general configuration topic in Configuring a MapR Gateway Master-Slave Topology is applicable, however, if you use the
maprcli cluster gateway set command, then the
-dstcluster parameter is set to the MapR source cluster.
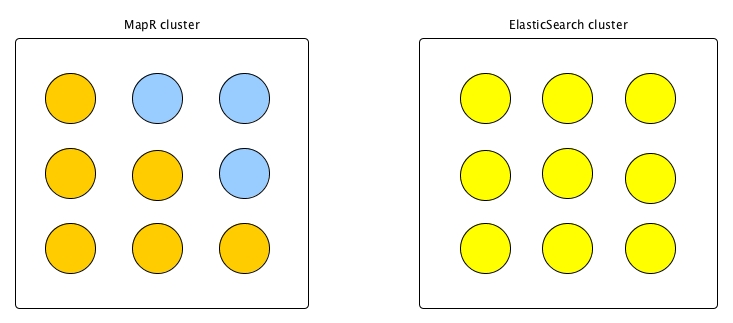
Gateways on Independent Nodes That Are Added to the Source MapR Cluster
In the next diagram, the gateways are installed on servers that were not previously part
of the MapR cluster. Only the gateway services are installed on these new nodes.
However, these nodes logically become part of the MapR cluster, as indicated by the
dotted line extending from this cluster. Because gateways consume CPU and network
resources, placing gateways on dedicated nodes allows for higher throughput rates than
the previous configuration. If you use this topology then the configuration topic in
Configuring a MapR Gateway on an Independent Node for Elasticsearch Indexing is
applicable. If you use the maprcli cluster gateway set command, then
the -dstcluster parameter is set to the MapR source cluster.
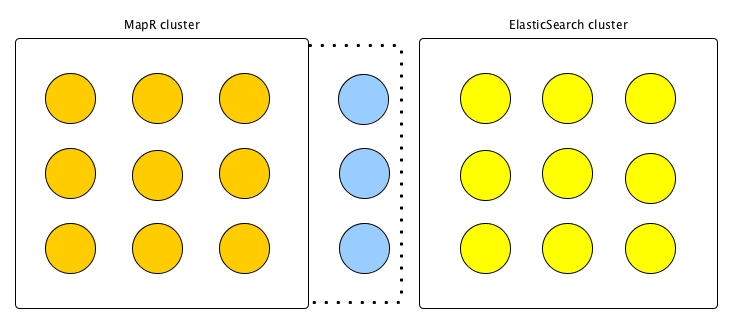
Gateways on the Elasticsearch Cluster
In the final diagram, the gateways are installed on nodes that are part of the
Elasticsearch cluster. As in the previous diagram, these nodes logically become part of
the MapR cluster, as again indicated by the dotted line extending from the MapR cluster.
The gateways are managed from that cluster only. No management of the gateways needs to
take place through Elasticsearch. If you use this topology then the configuration topic
in Configuring a MapR Gateway on an Independent Node for Elasticsearch Indexing is
applicable. If you use the maprcli cluster gateway set command, then
the -dstcluster parameter is set to the MapR source cluster.